二叉树
二叉树
基本概念
结构描述
class Node{
value:any,
left:Node,
right:Node
}
二叉树(Binary tree)是树形结构的一个重要类型,二叉树特点是每个结点最多只能有两棵子树,且有左右之分,形态如下图
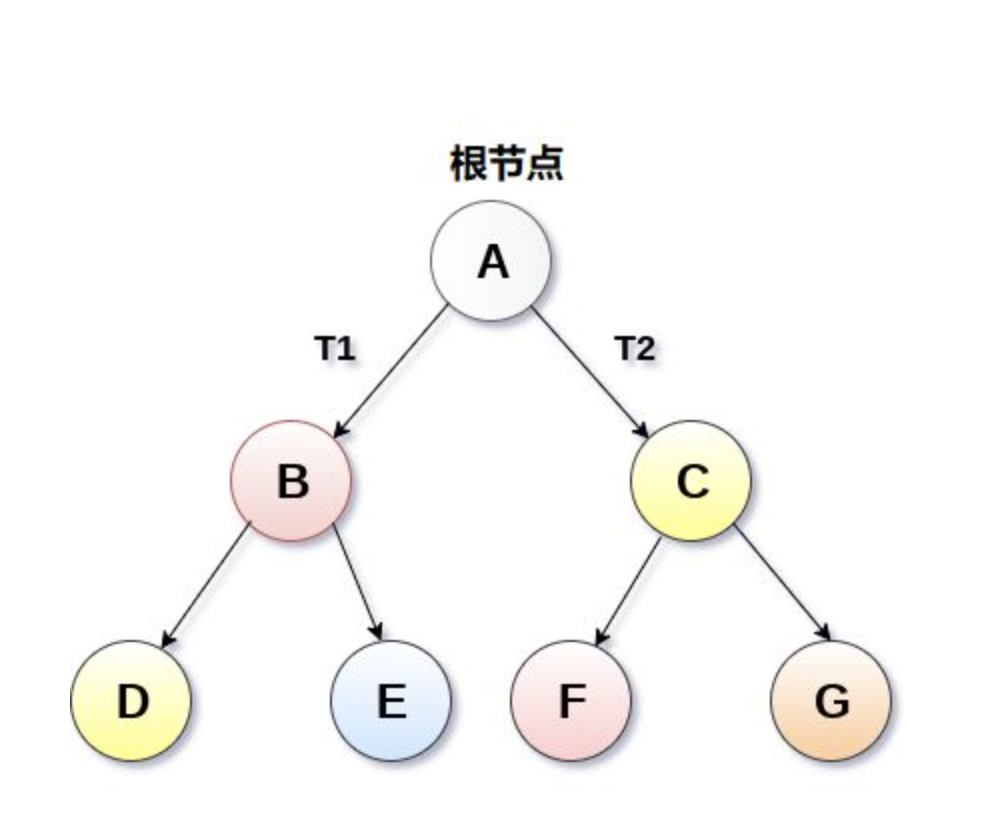
二叉树的深度优先遍历
- 先序遍历
任何子树的处理顺序都是,先头节点,再左子树,再右子树
- 中序遍历
任何子树的处理顺序都是,先左子树,再头节点,再右子树
- 后序遍历
任何子树的处理顺序都是,先左子树,再右子树,再头节点
exp: 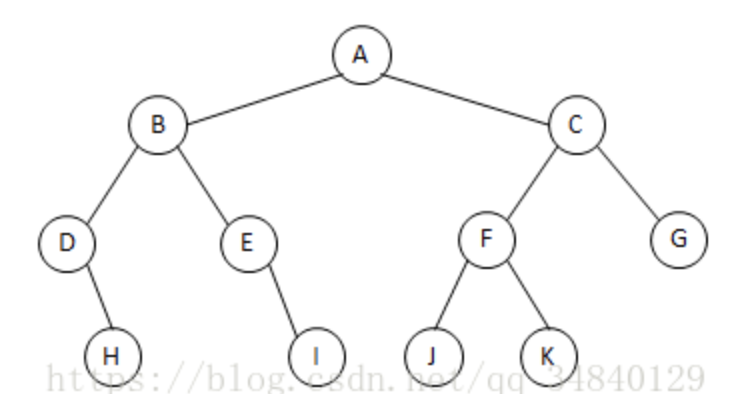
先序遍历(根左右):A B D H E I C F J K G
中序遍历(左根右) : D H B E I A J F K C G
后序遍历(左右根) : H D I E B J K F G C A
以后(根)序遍历为例,每次都是先遍历树的左子树,然后再遍历树的右子树,最后再遍历根节点,以此类推,直至遍历完整个树。
代码实现
//先序遍历
function pre(node){
if(node == null){
return
}
console.log(node.value)
pre(node.left)
pre(node.right)
}
//中序遍历
function in(node){
if(node == null){
return
}
in(node.left)
console.log(node.value)
in(node.right)
}
//后序遍历
function pos(node){
if(node == null){
return
}
pos(node.left)
pos(node.right)
console.log(node.value)
}
二叉树的递归序
function pos(node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
// console.log(node.value)放这里是先序遍历
pos(node.left);
// console.log(node.value)放这里是中序遍历
pos(node.right);
// console.log(node.value) 放这里是后序遍历
}
通过上面代码我们发现 console.log 放到不同的位置,就会触发不同的打印结果,假设我们要遍历的二叉树如下图
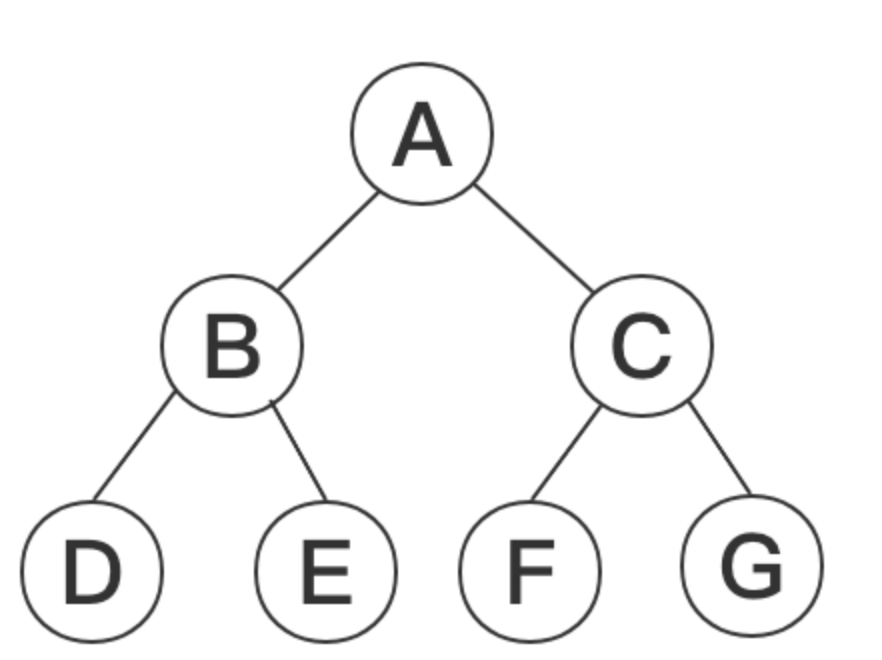
上述代码运行,递归序列:A B D D D B E E E B A C F F F C G G G C A 递归顺序如下图所示
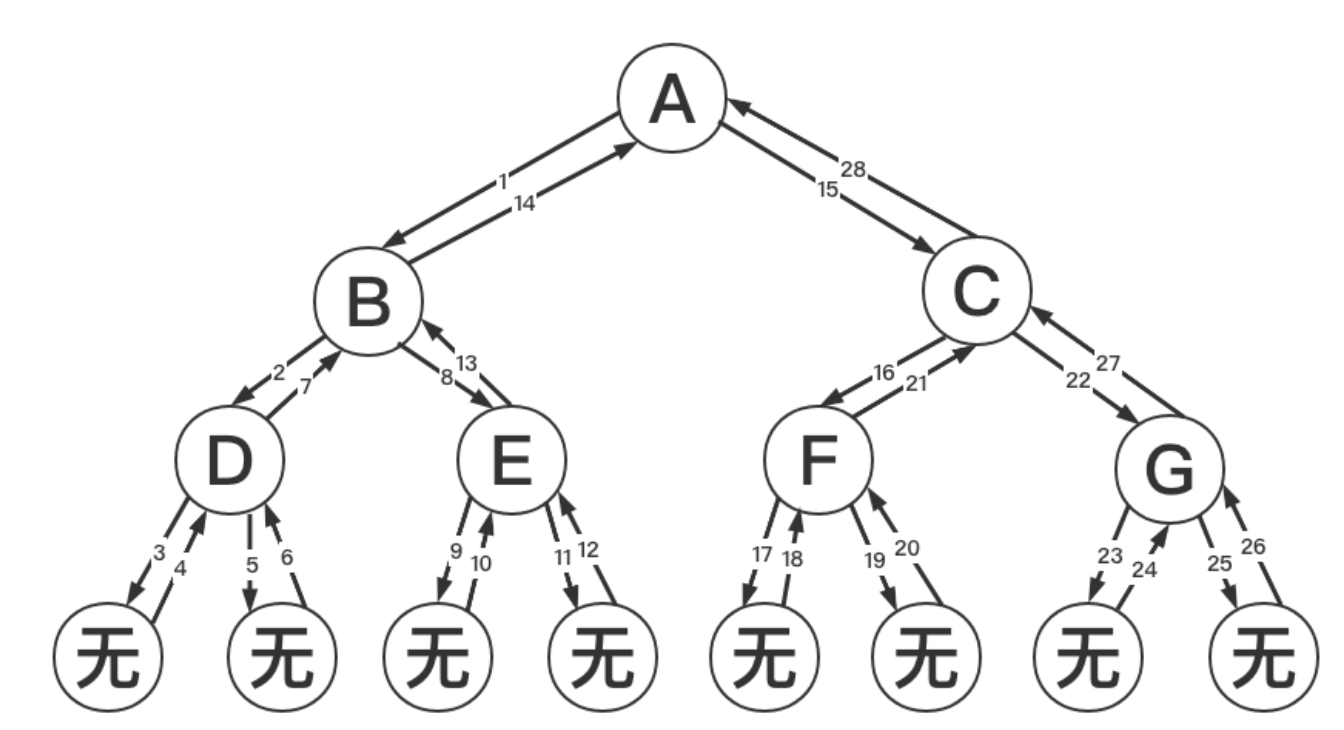
先序遍历:第一次经过时打印,先序序列:A B D E C F G
中序遍历:第二次经过时打印,中序序列:D B E A F C G
后序遍历:第三次经过时打印,后序序列:D E B F G C A
从上面过程可以发现每个节点都会返回三次
非递归方式实现二叉树的先序,中序,后序遍历
任何递归函数都可以改成非递归
通过自己设计压栈(后进先出)来实现
- 先序遍历(头左右) 1)弹打印 2)如有右,压入右 3)如有左,压入左
function pre(node: Node) {
if (node == null) return;
const stack: Node[] = [];
stack.push(node);
while (stack.length !== 0) {
const stackTop = stack.pop();
console.log(stackTop.value);
if (stackTop.right) {
stack.push(node.right);
}
if (stackTop.left) {
stack.push(node.left);
}
}
}

- 后序遍历
1)弹打印 2)如有左,压入左 3)如有右,压入右
头右左的逆序就是左右头
function pos(node: Node) {
if (node == null) return;
const stack1: Node[] = [];
const stack2: Node[] = [];
stack1.push(node);
while (stack1.length !== 0) {
const stackTop = stack1.pop();
stack2.push(stackTop);
if (stackTop.left) {
stack1.push(node.left);
}
if (stackTop.right) {
stack1.push(node.right);
}
}
while (stack2.length !== 0) {
console.log(stack2.pop().value);
}
}
- 中序遍历
1)整个左边界依次进栈 2)左边界无法进站,弹出栈顶打印该节点,在该节点右树继续左边界依次进栈,如果不成立继续执行条件 2
function in(head:Node){
if(head==null)return;
const stack:Node[] = [];
while(head!=null&&stack.length!=0){
if(head!=null){
stack.push(head)
head = head.left
}else{
head = stack.pop();
console.log(head.value);
head = head.right;
}
}
}

二叉树的按层遍历(广度优先遍历)
用队列实现,可以通过设置 flag 变量的方式,来发现某一层的结束
function level(node: Node) {
const queue: Node[] = [];
queue.push(node);
while (queue.length > 0) {
const queueHead = queue.shift();
console.log(queueHead.value);
if (queueHead.left) {
queue.push(queueHead.left);
}
if (queueHead.right) {
queue.push(queueHead.right);
}
}
}
实例:获取二叉树的最大宽度 使用 Map 方式:
function getTreeMaxWidth(node: Node) {
if (node == null) return;
const queue: Node[] = [];
queue.push(node);
const max = 0; //最大宽度
const curEnd = node; //当前层的最后节点
const nextEnd = null; //下一层的最后节点
const curLevelNum = 0; //当前层的数量
while (queue.length !== 0) {
const queueHead = queue.shift();
console.log(queueHead.value);
if (queueHead.left) {
queue.push(queueHead.left);
nextEnd = queueHead.left;
}
if (queueHead.right) {
queue.push(queueHead.right);
nextEnd = queueHead.right;
}
curLevelNum++;
if (queueHead == curEnd) {
//如果当前弹出节点是当前的最后节点,代表本层结束
max = Math.max(max, curLevelNum);
curEnd = nextEnd;
curLevelNum = 0;
}
}
return max;
}
二叉树的序列化和反序列化
1)可以用先序,中序,后序或者按层遍历,实现二叉树的序列化
2)用了什么方式序列化,就要通过什么方式反序列化
如果树不全,一定要用 null 进行补全
- 深度优先遍历的序列化
//先序遍历的实现
function serialize(node: Node) {
const serial: any[] = [];
function pre(node) {
if (node == null) {
serial.push(null);
} else {
serial.push(node.value);
pre(node.left);
pre(node.right);
}
}
pre();
return serial;
}
- 深度优先遍历的反序列化
function deSerialization(serial: any[]) {
const value = serial.pop();
if (value == null) {
return null;
}
const head = new Node(value);
head.left = deSerialization(serial);
head.right = deSerialization(serial);
return head;
}
deSerialization(serial);
- 广度优先遍历的序列化
function serialize(node: Node) {
const serialList: any[] = [];
const stack: Node[] = [];
stack.push(node);
function level(node) {
while (stack.length > 0) {
const stackHead = stack.pop();
if (!stackHead) {
serialList.push(null);
} else {
serialList.push(stackHead.value);
stack.push(stackHead.left);
stack.push(stackHead.right);
}
}
}
pre();
return serialList;
}
- 广度优先遍历的反序列化
function deSerialize(serialList: any[]) {
if (serialList == null || serialList.length == 0) return null;
const head = generateNode(serialList.pop());
const queue: Node[] = [];
if (head !== null) {
queue.add(head);
}
let node = null;
while (queue.length > 0) {
node = queue.pop();
node.left =generateNode(serialList.pop());
node.right = generateNode(serialList.pop());
if (node.left != null) {
queue.push(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.push(node.right);
}
}
return head;
}
function generateNode(val:string){
if(val==null) return null;
return new Node(val)
}
deSerialize(serialList);
